What's Really Dangerous About Phishing?
In this blog post, we'll explore what happens when you interact with phishing emails. Our aim is simple: to address the pressing question - just how risky is it to interact with phishing emails? We'll discuss the dangers of opening, clicking, and sharing information in these emails. Additionally, we'll debunk some common myths about cybersecurity to provide a clearer understanding of the role of training. To keep things simple, we'll focus solely on email-based phishing, leaving out other methods like SMS or social media scams.
What is phishing?
Phishing, in its simplest form, is a fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or personal identification. They do this by pretending to be someone you trust, like a bank or a company you know. They'll send emails, texts, or messages on social media that seem real, but they're actually trying to deceive you.

The deceptive nature of phishing
Phishing is all about deception. Cybercriminals send messages that appear genuine, using psychological tactics to exploit human vulnerabilities. Whether it's exploiting fear with urgent requests or enticing curiosity with irresistible offers, these tactics play on our emotions, leading us to lower our guard and share sensitive information like passwords or credit card details.
Let's debunk common cybersecurity myths
In this section, we'll explore some widely believed myths surrounding cybersecurity. Before diving into the myths, let's clarify some key terms.
What is Antivirus software
This type of software is designed to prevent, detect, and remove viruses from computers. It continuously monitors programs for unusual behavior, cross-checks new files against known malware databases, and isolates threats before they can cause damage.
What is Anti-malware software
This is an umbrella term for software that safeguards systems from various forms of malware, including ransomware, spyware, adware, and other malicious software. Anti-malware software can intercept and prevent the installation of new malware (for instance, by scanning files during download) or identify, isolate, and eliminate existing malware.
What is VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN service establishes a secure, encrypted online connection, enhancing internet users' privacy and concealing their true location.
Now that we've defined the terms, it's time to debunk some common myths.
Myth: VPNs provide complete protection against phishing attacks
While VPNs offer valuable security features, they do not provide comprehensive defense against all phishing scenarios. Despite encrypting data and hiding IP addresses, most VPNs do not protect against malware, social engineering, or phishing attempts. Additionally, VPNs cannot prevent users from visiting phishing sites or inadvertently sharing sensitive data with hackers. If you download malware from a compromised website, it will run on your device even with an active VPN connection. If you click and submit data, the hacker still gets that information, even if you are using a VPN. They won’t see your actual IP address, but that’s not what they’re really after, anyway.
Myth: Anti-Malware software guarantees full defense against phishing attempts.
Although antivirus and anti-malware software are essential tools for device security, they cannot guarantee complete protection against all cyber threats. While these solutions help detect and remove known malware, they may not always provide up-to-date protection against evolving threats. Moreover, they do not prevent users from visiting fake websites or opening suspicious emails, leaving them vulnerable to phishing attacks. Getting users to install malware on their devices is just one desired phishing outcome. But the software does nothing for the type of phishing that aims to get a user's credentials or data
Myth: Two Factor Authentication protects you from all the negative phishing consequences
While Two Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of authentication to online accounts, it does not ensure complete security. While it protects login credentials, it does not prevent other consequences of phishing attacks, such as giving scammers access to information for targeted campaigns. Additionally, 2FA does not shield against malware infections or prevent users from inadvertently submitting sensitive data to hackers. 2FA only works for accounts it's set up for and if it’s used properly.
Myth: All external emails are clearly marked and safe
Despite many email systems marking external emails, this does not guarantee safety. Employees may become immune to warnings, leading them to overlook external email indicators. Moreover, effective social engineering tactics can overshadow these warnings, making users susceptible to phishing attempts.
Myth: Being on the company network or VPN guarantees security against phishing attacks.
While some organizations mandate network or VPN access for sensitive information, this does not guarantee security. Users may still be vulnerable to personal account breaches, exposure of VPN login instructions, and malware threats, even when connected to the company network or VPN.
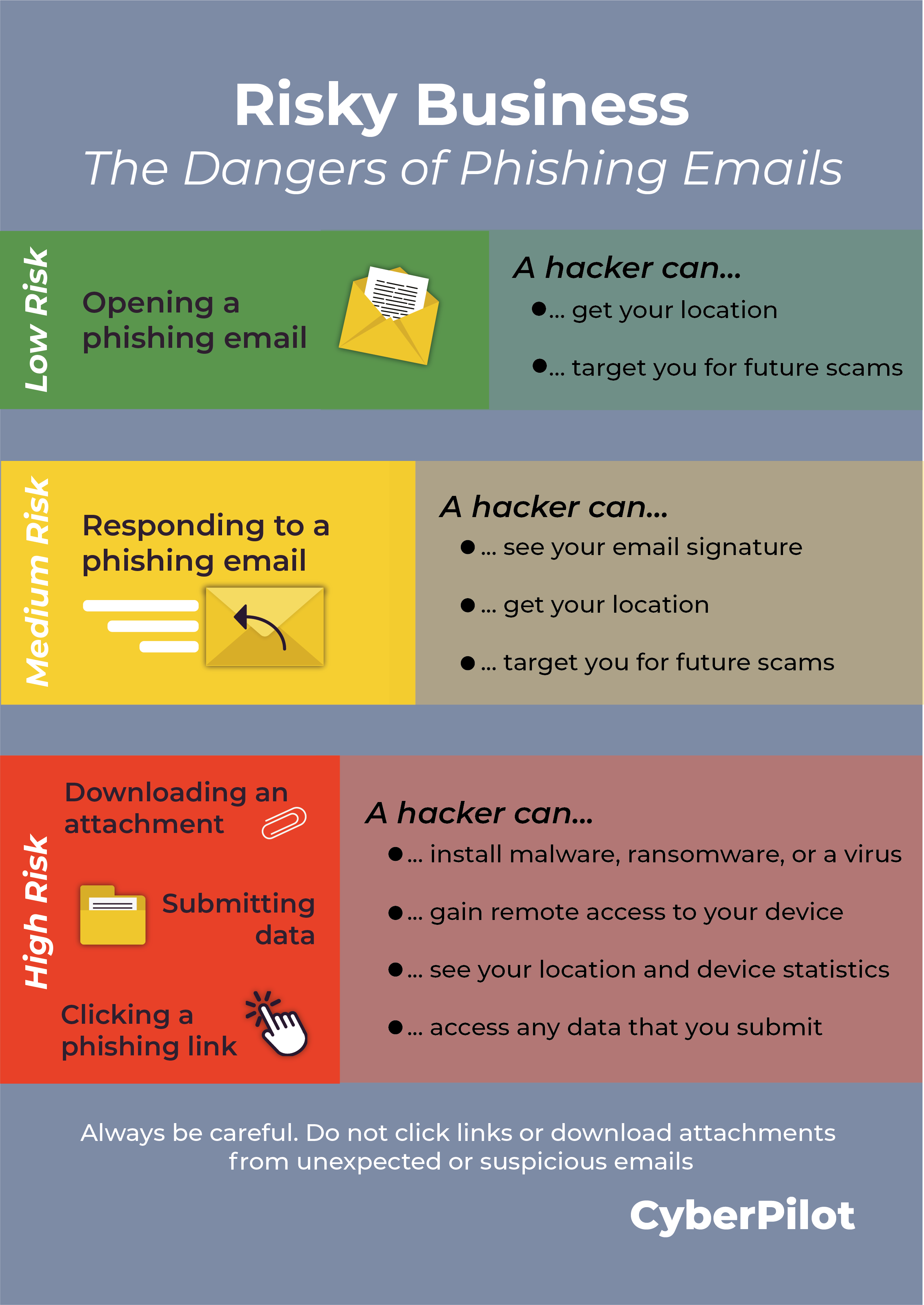
Understanding the dangers of interacting with phishing emails
Engaging with phishing emails involves risks. Just opening an email usually isn't too dangerous, but if you reply or preview attachments, there's some risk. The biggest risk comes from opening attachments, clicking links, or sharing data.
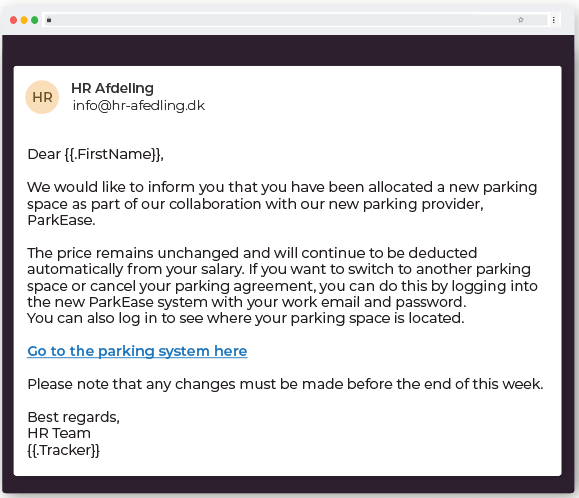
(This is an example of how a simulated phishing email sent from our phishing training could look like)
Now, let's delve into various phishing scenarios, examining their consequences and threat levels.
What happens if you open a phishing email?
When you open a phishing email, the scammer can collect information about you, potentially using it for future targeted attacks. By opening the email, you confirm to the scammer that your email address is active and that you're a real person. This opens the door for them to gather details like your IP address, operating system, and location. These details might seem minor, but they can be valuable for cybercriminals in crafting more convincing and targeted phishing attempts in the future.
Low threat level: Simply opening the phishing email poses minimal immediate risk to your device. It is unlikely that you will get a virus or malware just by opening a phishing email. Almost all viruses are activated when you download an attachment or click a link present in an email. However, you are flagging yourself to the hacker as a legitimate target and they could get your location. While the chances of immediate harm are low, the potential for future attacks is increased.
What happens if you respond to a phishing email?
When you reply to a phishing email, the scammer gains access to your email signature, potentially containing personal details like phone numbers and other information. This allows them to create more convincing email templates and identify new targets within your organization. Additionally, by responding, you confirm to the scammer that your email address is active, which could result in them selling it to other scammers. This means you may become a priority target for future scam attempts.
Medium threat level: Responding to a phishing email puts you at a higher risk than just opening it. By replying, you confirm to the scammer that you are a real and active target. They can use any information you provide, including your email signature, to craft more convincing phishing emails. Additionally, by interacting with the email, you may train your email provider's spam filters to allow similar scams into your inbox in the future.
What happens if you click on a phishing link but don’t submit data?
When you click on a phishing link, your device can be exposed to malware, ransomware, or viruses. This means the attacker can automatically obtain basic data like your device statistics, location, and any other information you may have voluntarily provided. Furthermore, the hacker may exploit your contacts and network to send phishing emails to your contact list or gain remote access to your device. It's important to note that ransomware, a type of malicious software, can also be installed through these links, potentially locking you out of your device or system until a ransom is paid.
High threat level: Clicking on a link in a phishing email is where the danger escalates significantly. This action can lead to the automatic installation of malware, ransomware, or viruses on your device. These malicious programs can spy on your activities, track your keystrokes, and compromise sensitive data such as login credentials and personal information. The consequences can include identity theft, breached accounts, and unauthorized access to systems or networks.
What happens if you click on a phishing link and submit data?
If you click on a phishing link and submit data, the consequences can be severe. The hacker obtains any information you provide, including login credentials, bank or credit card details, and more. Clicking on the phishing link also automatically sends basic data to the attacker, such as your device statistics, location, and any other information you might have voluntarily shared.
High threat level: Clicking on a link and submitting data in a phishing email is among the most dangerous actions you can take. It provides the scammer with direct access to sensitive information. This opens the door to identity theft, breached accounts, and potential business email compromise. The risk is heightened because the hacker now has verified and valuable information about you.
What happens if you preview an attachment in a phishing email?
When you preview an attachment in a phishing email, it's risky because it can trigger malware or other harmful software. Sometimes, just by previewing the attachment without even opening or downloading it, you can unknowingly activate malware. This gives the hacker a way into your device, which can lead to malware being installed, your personal information and passwords being compromised, system vulnerabilities being exploited, and even the potential for identity theft if the attachment includes phishing forms or asks for personal details.
Medium threat level: Even just previewing an attachment in a phishing email can pose risks. This seemingly innocent action can have serious consequences, such as compromising your personal information and passwords. In the worst-case scenario, it could even put you at risk of identity theft. Once malware is activated through the preview, it can start spying on your online activities, tracking what you type (including passwords), and granting cybercriminals access to your accounts and systems.
What happens if you download an attachment from a phishing email?
When you download an attachment from a phishing email, you expose yourself to risks. This action can install malware, ransomware, or a virus on your device. It might even launch a keylogger, a malicious tool designed to steal personal information like usernames, passwords, screenshots of your activity, and even your credit card numbers or bank details. If ransomware is present, it can lock you out of your device or system until you pay a ransom.
High threat level: Opening and downloading an attachment from a phishing email is one of the most dangerous actions. This action can directly install malware, ransomware, or viruses on your device, potentially launching a keylogger to steal personal information. The consequences can be severe, including compromised data, identity theft, and unauthorized access to your accounts and systems.
Understanding these scenarios and their potential consequences underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and ongoing vigilance against phishing attacks.
What should you do in case of a phishing incident?
Phishing emails can vary in severity, from low-risk to high-risk scenarios. Here's what you should do if you encounter any of these situations.
If you open a phishing email
Instead of just unsubscribing, mark the email as junk. This helps your email client recognize and filter out malicious emails in the future. Take a moment to scan your device for ransomware, trojan horse viruses, and other malware.
If you respond to a phishing email
Trust your instincts and avoid replying to suspicious emails. Report the email as phishing to your email provider. It's also a good idea to educate yourself and others about common phishing tactics.
If you click on a phishing link
Act fast and disconnect from the internet to prevent further data transmission. Run your antivirus software to scan your device thoroughly. Consider changing passwords for sensitive accounts for added security.
If you submit data in a phishing email
Disconnect immediately and change passwords for any accounts where you submitted information. Don't hesitate to report the incident to your organization's IT department—they're there to help.
If you preview an attachment
Trust your instincts and don't open any suspicious attachments. Delete the email and empty the trash. It's also a good idea to run a full system scan with your antivirus software.
If you download an attachment
Avoid opening the attachment if possible. Disconnect from the internet and run a full system scan with reputable antivirus software to catch any potential threats.
Remember, cybersecurity is crucial. By staying vigilant and taking these steps, you can protect yourself and your information from falling into the wrong hands.
How can you protect your company against phishing attacks?
Phishing scams pose a serious risk to businesses today, offering cybercriminals a deceptive way to steal valuable information. So, how can you protect your company from these threats? Here are three essential steps to consider:
Provide comprehensive awareness training
Ensure all team members understand what phishing is and how to spot it. Even the best security software can't prevent human error, so it's crucial to educate employees on identifying phishing emails and avoiding these traps. Regular discussions and including phishing awareness in new employee training can help strengthen your defenses.
Implement phishing training
Phishing training is a key component of effective cybersecurity for your organization. It equips employees with the knowledge to recognize phishing attempts, steer clear of harmful links, and report suspicious activity promptly. This training not only prevents malware infections and data breaches but also fosters a culture of vigilance within your company.
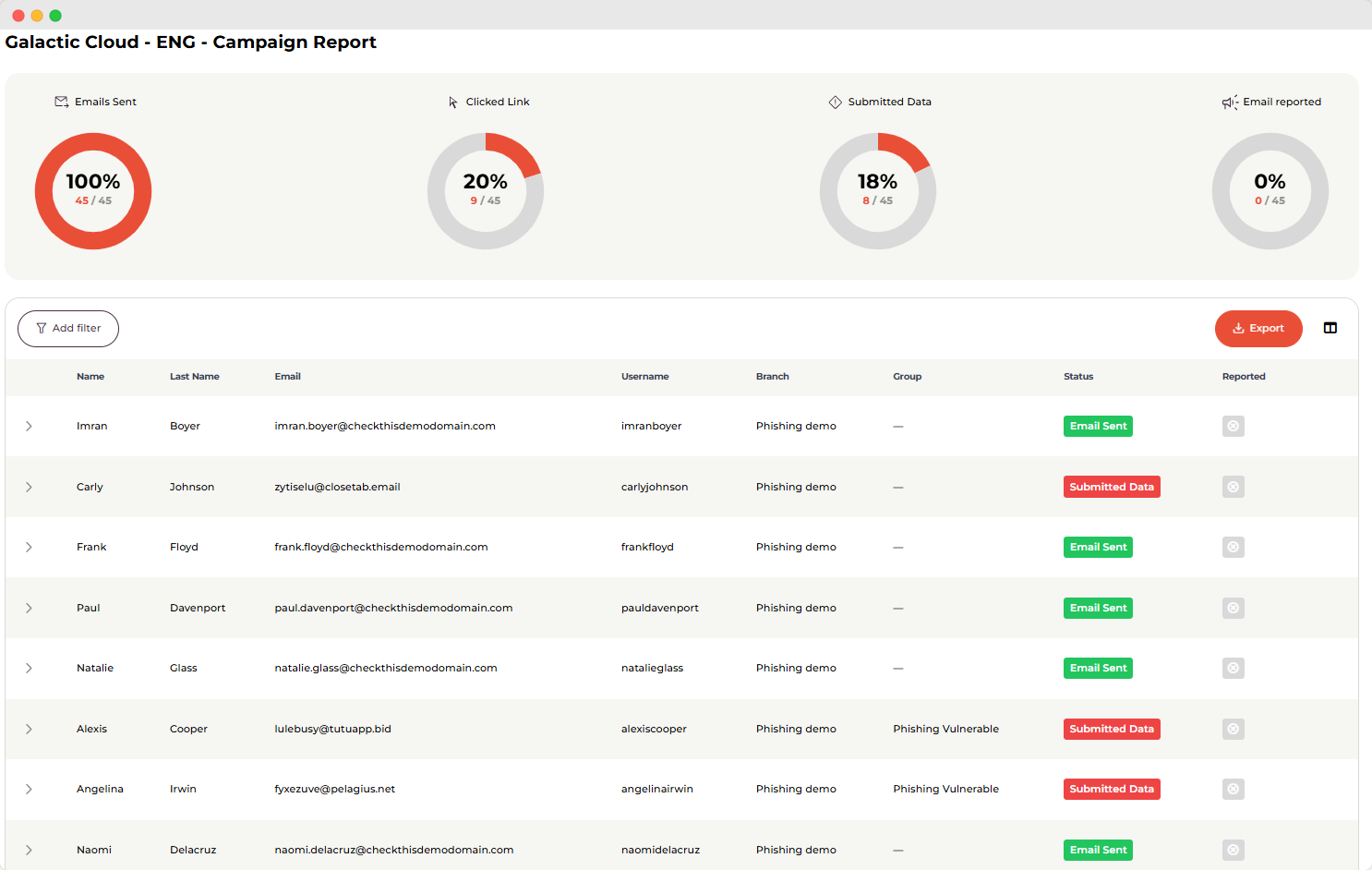
(This is an example of how you can track results from our simulated phishing training in our platform)
Keep software updated
Make sure all your software is up to date. This includes your computer's operating system, web browsers, and any other programs you use. Software updates often contain fixes for security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. By keeping everything up to date, you're closing the door to potential security risks and making it harder for cybercriminals to sneak in.
At CyberPilot, we're here to help keep your business safe from phishing scams. Want to see if your team can spot a phishing email? Try our phishing training or get in touch for a free demo with one of our phishing experts.
You will receive inspiration, tools and stories about good cyber security practice directly in your inbox. Our newsletter is sent out approximately once a month.




.png?length=800&name=EP17_%20The%208%20tells%20of%20a%20phishing%20email%20you%20and%20your%20colleagues%20should%20know%20-%20or%20else...%20%20(1).png)


